Publications
2025
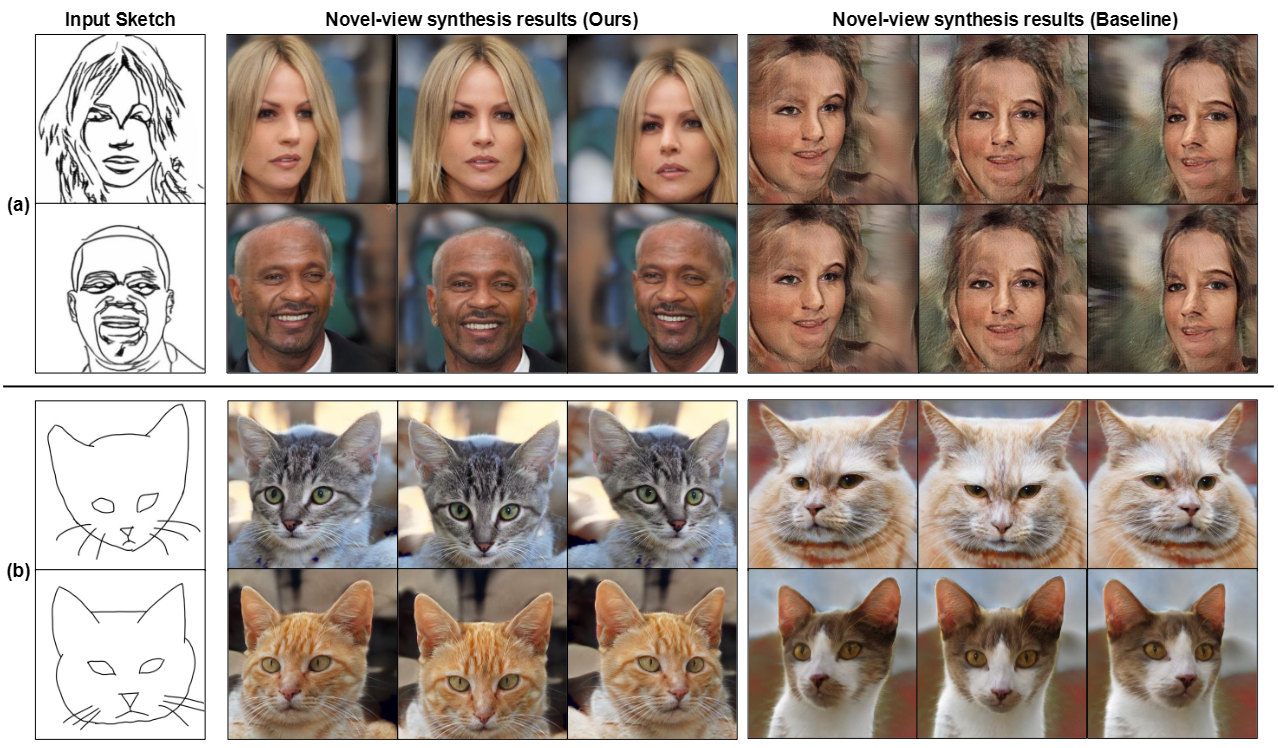
S3D: Sketch-Driven 3D Model Generation (CVPRW 2025, GMCV Workshop)
Hail Song*, Wonsik Shin*, Naeun Lee, Soomin Chung, Nojun Kwak, Woontack Woo

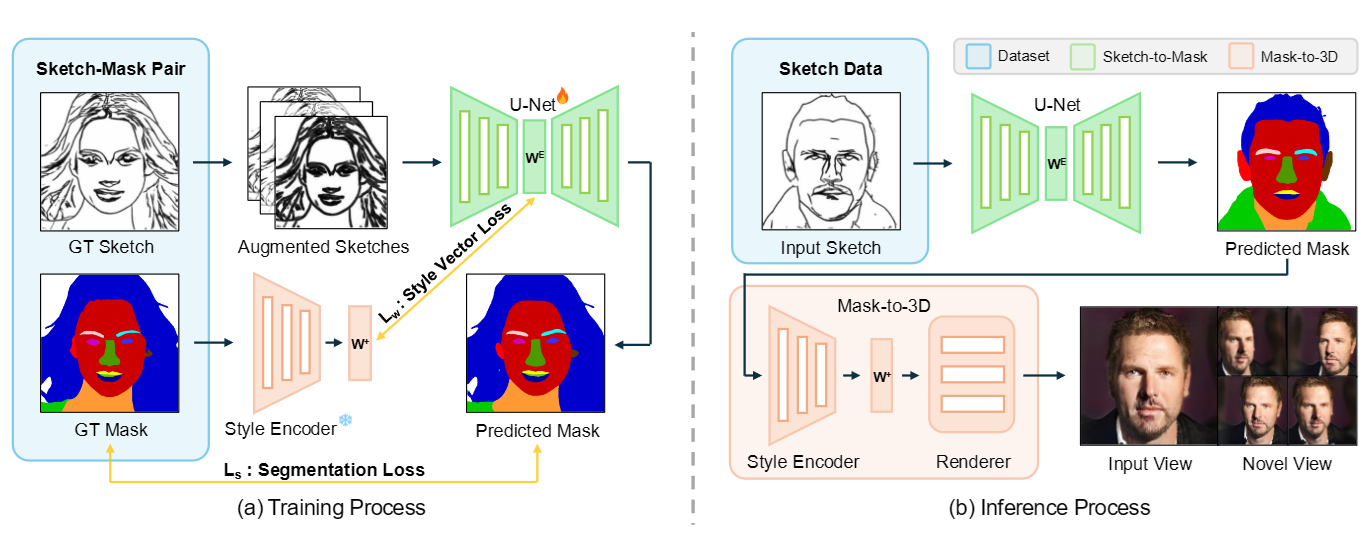
Abstract
*Generating high-quality 3D models from 2D sketches is a challenging task due to the inherent ambiguity and sparsity of sketch data. In this paper, we present S3D, a novel framework that converts simple hand-drawn sketches into detailed 3D models. Our method utilizes a U-Net-based encoder-decoder architecture to convert sketches into face segmentation masks, which are then used to generate a 3D representation that can be rendered from novel views. To ensure robust consistency between the sketch domain and the 3D output, we introduce a novel style-alignment loss that aligns the U-Net bottleneck features with the initial encoder outputs of the 3D generation module, significantly enhancing reconstruction fidelity. To further enhance the network's robustness, we apply augmentation techniques to the sketch dataset. This streamlined framework demonstrates the effectiveness of S3D in generating high-quality 3D models from sketch inputs.*
2024
Toward Realistic 3D Avatar Generation with Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting for AR/VR Communication (IEEE VRW, Best DC Paper Awards)
Hail Song
Abstract
*Realistic avatars are fundamental for immersive experiences in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) environments. In this work, we introduce a novel approach for avatar generation, combining 3D Gaussian Splatting with the parametric body model, SMPL. This methodology overcomes the inefficiencies of traditional image/video-based avatar creation, which is often slow and requires high computing resources. The integration of 3D Gaussian Splatting for representing human avatar offers realistic and real-time rendering for AR/VR applications. We also conducted preliminary tests to verify the quality of avatar representation using 3D Gaussian Splatting. These tests, displayed alongside outcomes from existing methods, demonstrate the potential of this research to significantly contribute to the creation of realistic avatars in the future. Additionally, several key discussions are presented, essential for developing and evaluating the system and providing valuable insights for future research.*
2023
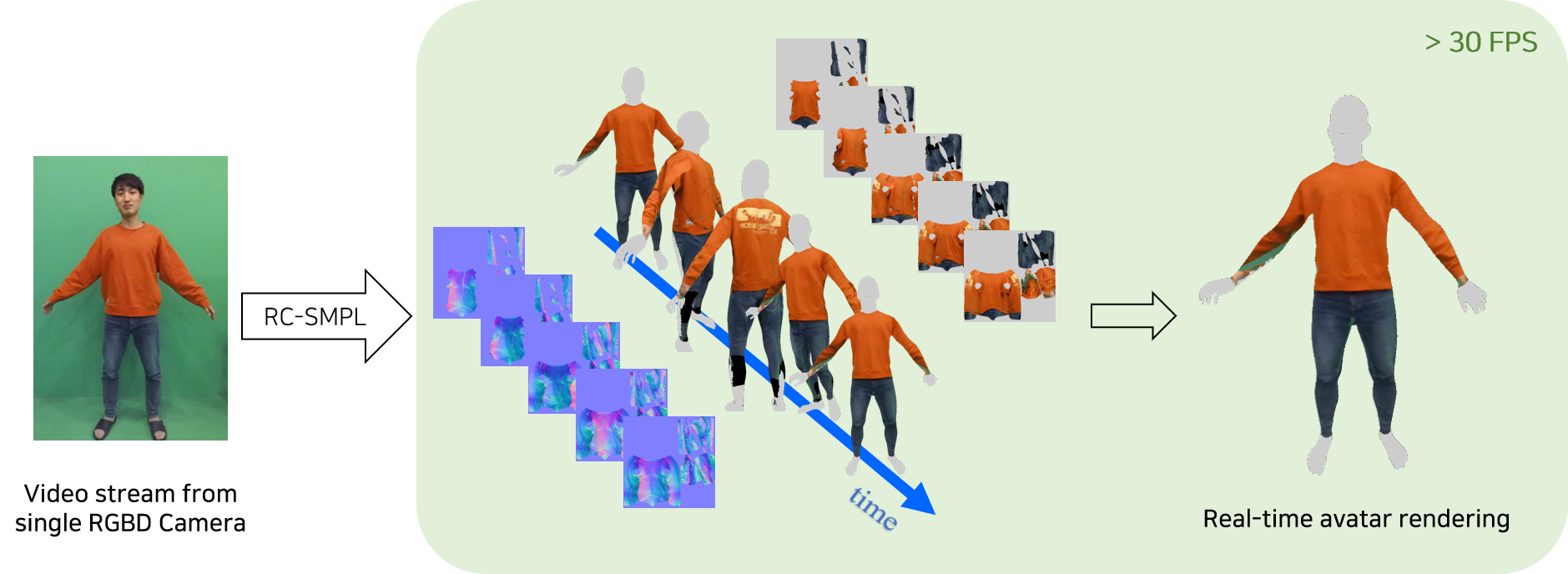
RC-SMPL : Real-time Cumulative SMPL-based Avatar Body Generation (IEEE ISMAR 2023)
Hail Song, Boram Yoon, Woojin Cho, Woontack Woo
Code / Youtube / Paper / Appendix
Abstract
*We present a novel method for avatar body generation that cumulatively updates the texture and normal map in real-time. Multiple images or videos have been broadly adopted to create detailed 3D human models that capture more realistic user identities in both Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) environments. However, this approach has a higher spatiotemporal cost because it requires a complex camera setup and extensive computational resources. For lightweight reconstruction of personalized avatar bodies, we design a system that progressively captures the texture and normal values using a single RGBD camera to generate the widely-accepted 3D parametric body model, SMPL-X. Quantitatively, our system maintains real-time performance while delivering reconstruction quality comparable to the state-of-the-art method. Moreover, user studies reveal the benefits of real-time avatar creation and its applicability in various collaborative scenarios. By enabling the production of high-fidelity avatars at a lower cost, our method provides more general way to create personalized avatar in AR/VR applications, thereby fostering more expressive self-representation in the metaverse.*
Effects of Different Facial Blendshape Combinations on Social Presence for Avatar-mediated Mixed Reality Remote Communication (IEEE ISMAR 2023 Poster)
Seoyoung Kang, Hail Song, Boram Yoon, Kangsoo Kim, Woontack Woo
Abstract
*Despite the significance of facial expressions in avatar-mediated communication, there has been limited research on efficiently representing avatar facial expressions, encompassing both computational and communicative considerations. To address this, we first conduct an analysis of facial blendshapes, where we select those based on activation variance during natural conversations and their significance in conveying emotions. From two distinct selection approaches, we then investigate the impacts of four different facial blendshape combinations on social presence and communication quality in varied avatar-mediated remote communication contexts: informative speech and emotional conversation. The results of our formal study with 32 participants highlight the importance of emotion-based blendshapes, indicating that the emotionally essential blendshapes combination achieves comparable levels of social presence, facial animation realism, communication quality, and synchrony of communication cues compared to using the full set of blendshapes. Our findings emphasize the potential of a cost-efficient method for avatar facial control, enabling effective emotional expressions while reducing computational resources, ultimately resulting in more affordable and efficient avatar-mediated communication experiences.*
Contact: hail96@kaist.ac.kr